GUM DISEASE
Q What is gum disease?
A Gum disease describes swelling, soreness or infection of the tissues supporting the teeth. There are two main forms of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontal disease.
Q What is gingivitis?
A Gingivitis means inflammation of the gums. This is when the gums around the teeth become very red and swollen. Often the swollen gums bleed when they are brushed during cleaning.
Q What is periodontal disease?
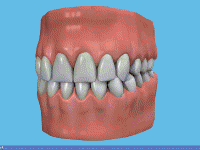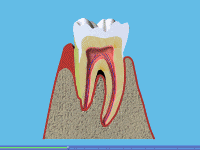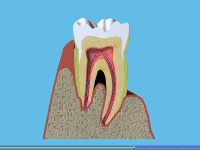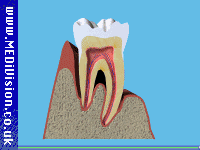
A Long-standing gingivitis can turn into periodontal disease. There are a number of types of periodontal disease and they all affect the tissues supporting the teeth. As the disease gets worse the bone anchoring the teeth in the jaw is lost, making the teeth loose. If this is not treated, the teeth may eventually fall out.
Q Am I likely to suffer from gum disease?
A Probably. Most people suffer from some form of gum disease, and it is the major cause of tooth loss in adults. However, the disease develops very slowly in most people, and it can be slowed down to a rate that should allow you to keep most of your teeth for life.
Q What is the cause of gum disease?
A All gum disease is caused by plaque. Plaque is a film of bacteria, which forms on the surface of the teeth and gums every day. Many of the bacteria in plaque are completely harmless, but there are some that have been shown to be the main cause of gum disease. To prevent and treat gum disease, you need to make sure you remove all the plaque from your teeth every day. This is done by brushing and flossing.
Q What happens if gum disease is not treated?
A Unfortunately, gum disease progresses painlessly on the whole so that you do notice the damage it is doing. However, the bacteria are sometimes more active and this makes your gums sore. This can lead to gum abscesses, and pus may ooze from around the teeth. Over a number of years, the bone supporting the teeth can be lost. If the disease is left untreated for a long time, treatment can become more difficult.
Q How do I know if I have gum disease?
A The first sign is blood on the toothbrush or in the rinsing water when you clean your teeth. Your gums may also bleed when you are eating, leaving a bad taste in your mouth. Your breath may also become unpleasant.
Q What do I do if I think I have gum disease?
A The first thing to do is visit your dentist for a thorough check-up of your teeth and gums. The dentist can measure the cuff of gum around each tooth to see if there is any sign that periodontal disease has started. X-rays may also be needed to see the amount of bone that has been lost. This assessment is very important, so the correct treatment can be prescribed for you.
Q What treatments are needed?
A Your dentist will usually give your teeth a thorough clean. Youll also be shown how to remove plaque successfully yourself, cleaning all surfaces of your teeth thoroughly and effectively. This may take a number of sessions with the dentist or hygienist.
Q What else may be needed?
A Once your teeth are clean, your dentist may decide to carry out further cleaning of the roots of the teeth, to make sure that the last
pockets of bacteria are removed.
Youll probably need the treatment area to be numbed before
anything is done. Afterwards, you may feel some discomfort for up to 48 hour.
Q Once I have had periodontal disease, can I get it again?
A Periodontal disease is never cured. But as long as you keep up the home care you have been taught, any further loss of bone will be very slow and it may stop altogether. However, you must make sure you remove plaque every day, and go for regular check ups by the dentist and hygienist.

